How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, the importance of pre-flight checks, and the nuances of controlling your aircraft.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial for responsible operation. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone , which will help you develop your skills and confidence. Ultimately, mastering how to operate a drone requires practice and a commitment to safe flying procedures.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will cover everything from basic flight maneuvers and essential pre-flight preparations to more advanced techniques like precise positioning and flying in challenging conditions. Understanding drone regulations is paramount, and we’ll provide a clear overview of the legal framework governing drone usage in various regions. Beyond the technical aspects, we’ll also explore the creative possibilities of aerial photography and videography, helping you capture breathtaking images and videos from unique perspectives.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to both legal regulations and crucial safety procedures. These guidelines ensure safe flight operations and prevent accidents, protecting both the drone and its surroundings.
Drone Regulations by Region
Drone laws vary significantly across countries and regions. Regulations often cover aspects such as registration, licensing, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific rules of your location before each flight.
| Country/Region | Registration Requirements | Airspace Restrictions | Weight Limits |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Registration required for drones over 0.55 lbs (250g). | Restrictions near airports, stadiums, and other sensitive areas. | Generally no weight limits for recreational use, but commercial use has stricter limits. |
| Canada | Registration required for drones over 250g. | Similar restrictions to the US, with designated no-fly zones. | Weight limits influence licensing and operational requirements. |
| United Kingdom | Registration is not mandatory for all drones, but it is recommended. | Strict rules on flying near airports and populated areas. | Weight and operational categories determine regulations. |
Drone Safety Procedures
Safety protocols are paramount for successful and safe drone operation. These procedures cover pre-flight checks, in-flight maneuvers, and post-flight maintenance.
- Pre-flight: Check weather conditions, battery levels, and GPS signal. Inspect the drone for any damage. Plan your flight path and ensure you have clear airspace.
- During flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone. Avoid flying near people, buildings, or obstacles. Be mindful of wind conditions and adjust flight accordingly.
- Post-flight: Inspect the drone for any damage. Securely store the drone and its components. Download and review flight logs.
Drone Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive checklist minimizes the risk of accidents or malfunctions.
- Check battery charge levels.
- Inspect propellers for damage.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Review local airspace restrictions.
- Check weather conditions.
Drone Parts and Components

Understanding the function of each drone component is essential for effective operation and maintenance. This knowledge helps in troubleshooting and ensures safe flight.
Key Drone Components and Functions
A typical drone comprises several interconnected parts working in harmony.
- Frame: Provides structural support for all components.
- Motors: Drive the propellers, generating thrust.
- Propellers: Generate lift and control the drone’s movement.
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Regulate the speed of the motors.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, managing all aspects of flight.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and autonomous flight.
- Battery: Provides power to all components.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: Enables pilot control.
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos.
Drone Propeller Types and Flight Performance
Different propeller designs affect flight characteristics such as speed, efficiency, and maneuverability.
- Standard Propellers: Offer a balance of speed and efficiency.
- Slow-spinning Propellers: Ideal for quieter flight and longer battery life.
- High-pitch Propellers: Provide increased speed and maneuverability.
Battery Life and Management
Proper battery management is critical for safe and efficient drone operation. Overuse or improper charging can lead to battery damage or even fire.
- Use only manufacturer-approved batteries and chargers.
- Never overcharge or over-discharge batteries.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Monitor battery voltage during flight.
Internal Drone Component Diagram
A detailed diagram would illustrate the physical arrangement of the flight controller, ESCs, motors, battery, and other internal components within the drone’s chassis. The diagram would clearly show the connections and pathways between these essential elements.
Pre-Flight Setup and Calibration
Proper pre-flight setup and calibration are crucial for safe and accurate drone operation. These steps ensure the drone functions correctly and minimizes the risk of accidents.
Charging and Connecting a Drone Battery
- Ensure the battery is compatible with the drone.
- Connect the battery to the approved charger.
- Monitor the charging process and disconnect once fully charged.
- Carefully connect the charged battery to the drone, ensuring secure connection.
Calibrating the Drone’s Compass and Sensors
Calibration ensures accurate readings from the drone’s sensors, crucial for stable flight.
- Power on the drone and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for compass calibration (usually involves rotating the drone 360 degrees).
- Perform sensor calibration as instructed in the drone’s manual; this often involves leveling the drone and letting the sensors adjust.
Checking GPS Signal Strength, How to operate a drone
A strong GPS signal is vital for accurate positioning and stable flight, especially in autonomous modes.
- Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired before takeoff.
- Fly in an open area with a clear view of the sky for optimal GPS reception.
Essential Pre-Flight Checks
- Battery charge
- Propeller inspection
- GPS signal strength
- Compass calibration
- Gimbal calibration (if applicable)
- Visual inspection of the drone for any damage
- Radio transmitter connection
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic flight controls and maneuvers is fundamental to safe and competent drone operation. Mastering these skills forms the basis for more advanced techniques.
Drone Flight Controls
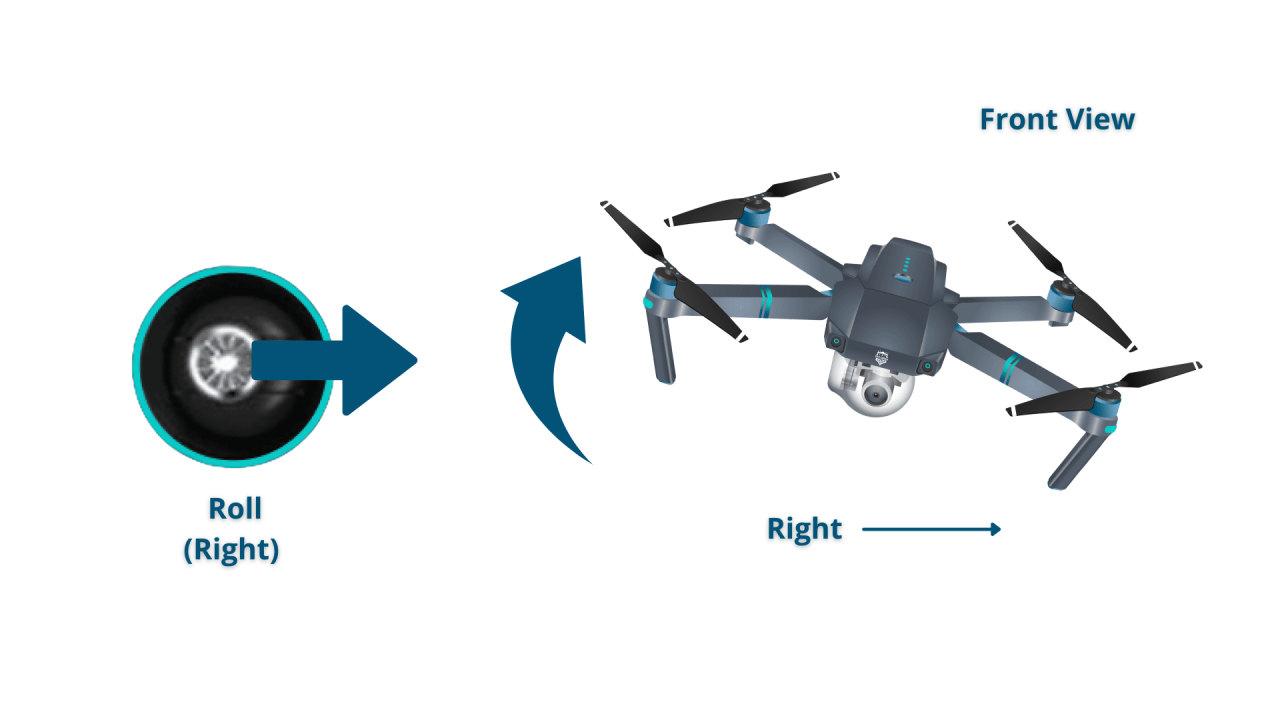
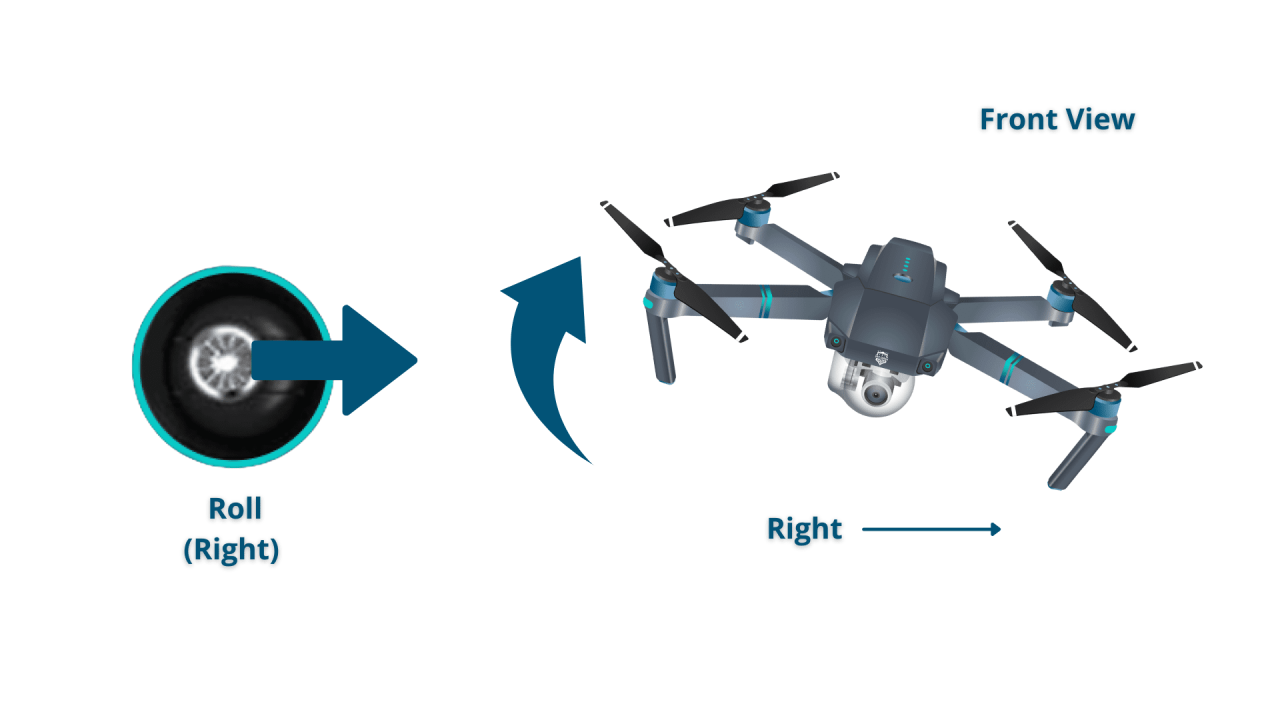
Most drones use joysticks or sticks for controlling pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle. Buttons on the controller provide additional functionalities like camera control and flight mode selection. Mode 1 and Mode 2 refer to the arrangement of these controls; Mode 1 is commonly used in the US, while Mode 2 is more prevalent in Europe.
Basic Flight Maneuvers

These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting.
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Landing: Gradually reduce throttle to lower the drone gently to the ground.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air.
- Directional Movement: Control the drone’s movement in any direction using the control sticks.
Comparison of Drone Control Schemes (Mode 1 vs. Mode 2)
Mode 1 and Mode 2 primarily differ in the assignment of the left and right sticks. Mode 1 (common in the US) uses the left stick for yaw and throttle, while the right stick controls pitch and roll. Mode 2 (common in Europe) reverses this assignment.
Flowchart of a Typical Drone Flight
A flowchart would visually represent the sequence of actions involved in a typical drone flight, from pre-flight checks and takeoff to landing and post-flight procedures. The flowchart would include decision points based on factors like weather conditions and GPS signal strength.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enhance drone capabilities, enabling more creative and precise aerial operations. These techniques require practice and a thorough understanding of drone controls.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
- Circling: Smoothly maneuvering the drone in a circular path.
- Figure-Eights: Executing a figure-eight pattern in the air.
- Precise Positioning: Accurately placing the drone in a specific location.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a solid grasp of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become proficient in piloting your own drone safely and effectively.
Proper training is crucial before you take to the skies.
- GPS Mode: Relies on GPS for position holding and stability.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, irrespective of GPS.
- Manual Mode: Offers complete control but requires more skill.
Flying in Challenging Conditions
Flying in wind or rain requires adjusting flight techniques and being mindful of safety precautions.
- Wind: Reduce speed and compensate for wind drift.
- Rain: Avoid flying in heavy rain to prevent water damage.
Advanced Maneuver Practice Exercises
A series of exercises would gradually increase in difficulty, starting with simple maneuvers and progressing to more complex ones. These exercises would cover various flight modes and conditions.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. The right settings and angles can transform ordinary footage into stunning visuals.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
- Ensure the drone’s camera is properly calibrated and focused.
- Select appropriate camera settings based on lighting conditions.
- Use smooth and controlled movements to avoid shaky footage.
- Compose shots thoughtfully, considering angles and perspectives.
Importance of Camera Settings
Camera settings greatly impact the final image or video quality.
- Aperture: Controls depth of field.
- Shutter Speed: Affects motion blur.
- ISO: Impacts image noise.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
- Utilize leading lines to guide the viewer’s eye.
- Employ the rule of thirds for balanced composition.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
Camera Angles and Their Effects
Using a low-angle shot can emphasize the scale of a subject, while a high-angle shot can provide a broader perspective. A side-angle shot can highlight a subject’s features, while a bird’s-eye view provides an overall context.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This extends the drone’s lifespan and ensures safe operation.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, or damaged power system. | Check battery, replace battery if necessary, inspect power system for damage. |
| Poor GPS signal | Obstructed GPS signal, interference, or faulty GPS module. | Fly in open area, check for interference, replace GPS module if necessary. |
| Unstable flight | Faulty sensors, low battery, or wind conditions. | Calibrate sensors, check battery, adjust flight based on wind. |
| Propeller damage | Collision or impact. | Replace damaged propellers. |
Importance of Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular cleaning, inspections, and part replacements extend the drone’s lifespan and prevent unexpected malfunctions.
- Clean the drone after each flight.
- Inspect propellers, motors, and other components for damage.
- Replace worn or damaged parts promptly.
Replacing Drone Parts
Replacing parts requires following the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Improper installation can lead to malfunctions or damage.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone regulations, components, pre-flight procedures, flight controls, advanced techniques, and maintenance. By diligently following safety guidelines, consistently practicing flight maneuvers, and understanding the capabilities of your drone, you’ll be well-equipped to explore the exciting world of aerial flight.
Remember that continuous learning and responsible operation are key to enjoying the many benefits and possibilities that drones offer. Safe flying!
Q&A
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and obstacle avoidance capabilities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a lower-risk flight mode (like Attitude Mode), and bring the drone down slowly and carefully. Avoid sudden movements.
How do I clean my drone propellers?
Gently wipe propellers with a soft cloth and isopropyl alcohol to remove dirt and debris. Avoid using harsh chemicals.
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store batteries in a cool, dry place at approximately 50% charge to prolong their lifespan. Never leave them fully charged for extended periods.